
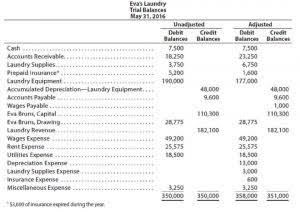
Future value (FV) is the value of a current asset at a future date based on an assumed rate of growth. It is important to investors as they present value of annuity table can use it to estimate how much an investment made today will be worth in the future. This would aid them in making sound investment decisions based on their anticipated needs. However, external economic factors, such as inflation, can adversely affect the future value of the asset by eroding its value. Given this information, the annuity is worth $10,832 less on a time-adjusted basis, so the person would come out ahead by choosing the lump-sum payment over the annuity. Because of the time value of money, money received today is worth more than the same amount of money in the future because it can be invested in the meantime.
Loan Amortization
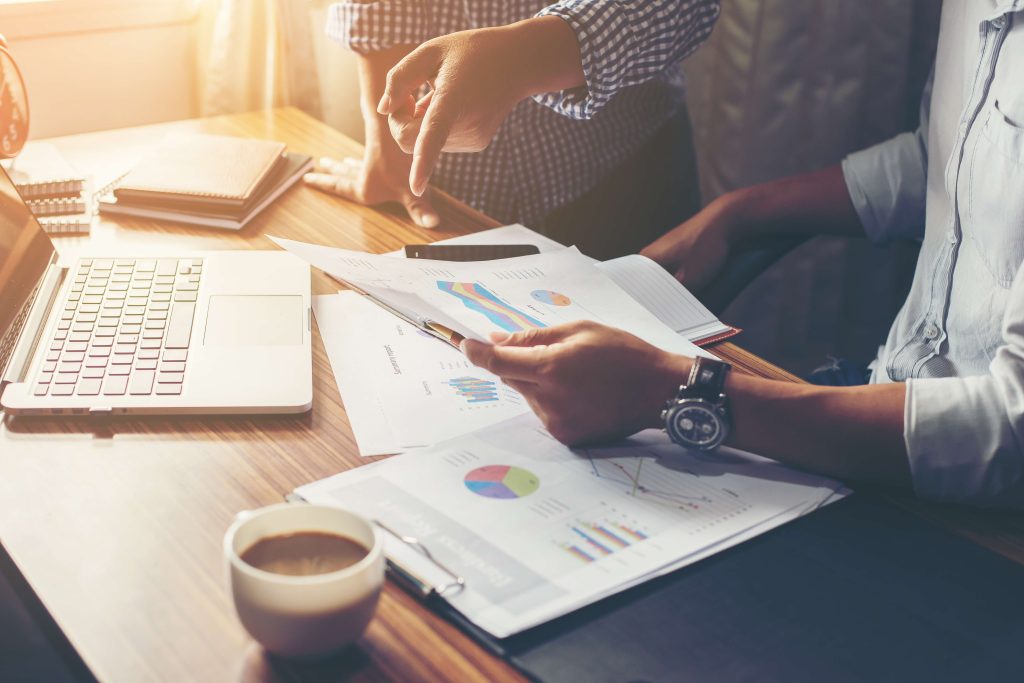
It lets you compare the amount you would receive from an annuity’s series of payments over time to the value of what you would receive for a lump sum payment for the annuity right now. Present value of annuity is the current value of an annuity’s future payments, discounted to reflect the time value of money. When calculated properly, it represents the present-day value of an annuity’s income stream. Present value and future value formulas help individuals determine what an ordinary annuity or an annuity due is worth now or later. Such calculations and their results help with financial planning and investment decision-making.

Types of Present Value Tables
The critical assumption of present value is that a dollar today is worth more than a dollar in the future. When comparing or evaluating annuities, present value is a way to place two or more different products on an equal standing and compare their present discounted values. An annuity table is a tool used mostly by accounting, insurance or other financial professionals to determine the present value of an annuity. An ordinary annuity generates payments at the end of the annuity period, while an annuity due is an annuity with the payment expected or paid at the start of the payment period. Given this information, the annuity is worth $10,832 less on a time-adjusted basis, and the individual should choose the lump sum payment over the annuity. Having $10,000 today is better than being given $1,000 per year for the next 10 years because the sum could be invested and earn interest over that decade.
How Do You Calculate Present Value Interest Factor for an Annuity?
Whether it’s free cash flow, dividend forecasts, or discount rates, the inputs are already there. This table is used when you’re receiving equal payments at the end of each period (like many bonds or rental payments). PV tables are great for quick estimates, but they’re locked to whatever AI in Accounting interest rates and time periods are printed on the page.
Any product that pays out at the end of a period is considered an ordinary annuity. The present value of an annuity is the current value of all future payments you will receive from the annuity. This comparison of money now and money later underscores a core tenet of finance – the time value of money.
These tables are easily “googlable”, but we’ve provided our own versions below. The first one here relates is a Present Value Discount Factor Table for single cash retained earnings flows (NOT annuities). You now know how to calculate Present Value of an Annuity using the formula and the annuity discount factor.
An annuity is a financial product that provides a stream of payments to an individual over a period of time, typically in the form of regular installments. Annuities can be either immediate or deferred, depending on when the payments begin. Immediate annuities start paying out right away, while deferred annuities have a delay before payments begin. Future value (FV) of annuity calculates the accumulated value of an annuity’s payments, plus interest, at a future point.

Present Value Interest Factor of Annuity (PVIFA) Formula, Tables
However, you can still use our present value of annuity calculator to solve more complex financial issues. In this section, you can familiarize yourself with this calculator’s usage and its mathematical background. An essential aspect of distinction in this present value of annuity calculator is the timing of payments. The formula, based on the potential interest rate and the number of payment periods, will give you a point of comparison between options. PV tables are used to provide a solution for the part of the present value formula shown in red, this is sometimes referred to as the present value factor.
- Let’s assume you want to sell five years’ worth of payments, or $5,000, and the factoring company applies a 10 percent discount rate.
- For example, you could use this formula to calculate the PV of your future rent payments as specified in your lease.
- Since this kind of annuity is paid only under a specific condition (i.e., the annuitant is still alive), it is known as a contingent annuity.
- The table considers how much money you have put into the annuity and how long it has been invested.
- Just to clarify, in the following annuity formulas, we refer to the ordinary annuity.
- Using the PVOA equation, we can calculate the interest rate (i) needed to discount a series of equal payments back to the present value.
Before we get to using the present value of annuity calculator, it is important to understand its formula to calculate the same. As discussed above, an annuity table helps you determine the present value of an annuity. Once you’ve found that number, you can make more informed investment decisions to build the best possible retirement portfolio for you. An annuity table helps you determine the present value of an annuity at a given time. The table considers how much money you have put into the annuity and how long it has been invested. Same deal as an ordinary annuity, but payments come at the beginning of each period (like lease payments or insurance premiums).

